datacamp에 좋은 강의가 많아서 파이토치 좀 본격적으로 배워보고 싶어 수강했다. 쏟은 시간으로는 5~6시간 정도 걸린 것 같다. 강의가 길진 않은데, 약간의 테스트랑 코드 파악하는데 시간을 좀 썼다. 정리하면서 까먹은 내용 다시 복기하고자 한다

Training Robust Neural Networks
Dataset과 Dataloader
class WaterDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, csv_path):
super().__init__()
# Load data to pandas DataFrame
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
# Convert data to a NumPy array and assign to self.data
self.data = df.to_numpy()
# Implement __len__ to return the number of data samples
def __len__(self):
return self.data.shape[0]
def __getitem__(self, idx):
features = self.data[idx, :-1]
# Assign last data column to label
label = self.data[idx, -1]
return features, labelUser-defined Dataset을 작성할 때에는 반드시 세 개의 메소드가 포함되어야 한다.
1. __init__()
2. __len__()
3. __getitem__()
# Create an instance of the WaterDataset
dataset_train = WaterDataset("water_train.csv")
# Create a DataLoader based on dataset_train
dataloader_train = DataLoader(
dataset_train,
batch_size=2,
shuffle=True,
)
# Get a batch of features and labels
features, labels = next(iter(dataloader_train))
print(features, labels)Datalodaer은 data를 wrapping해 주는 역할을 수행한다. batch의 크기나 shuffle 유무 등을 설정할 수 있다.
Training loop
1. loss함수, optimizer정의
2. epoch, training batch에 따라 반복
3. clear gradient
4. get model's outputs
5. compute loss
6. compute gradients
7. optimizer.step() : update parameters

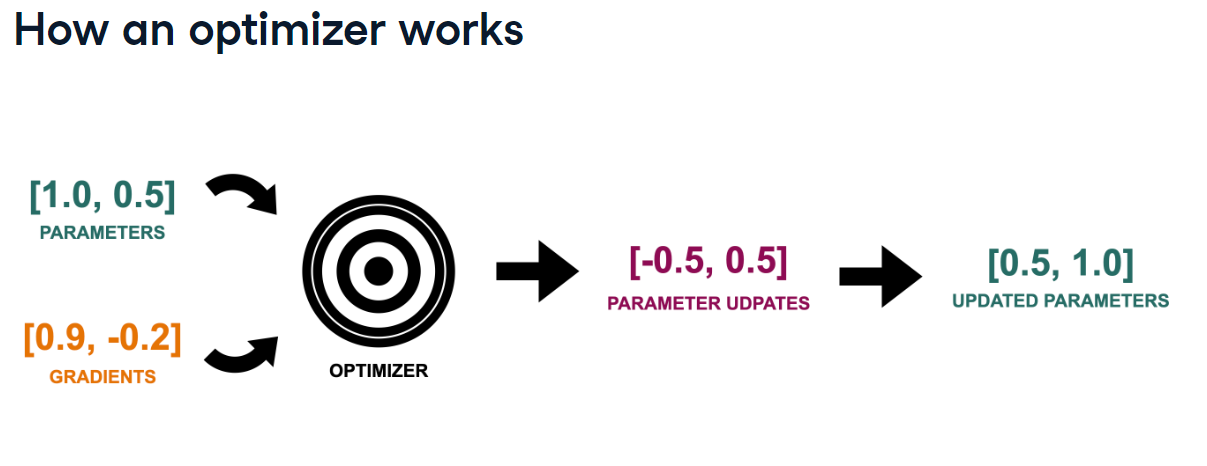
그럼, optimizer가 update할 방향과 양은 어떻게 알지?
방향 : gradient의 부호로 판단
첫 번째 파라미터 : 양의 기울기를 가지므로 손실을 줄이려면 이(0.9)를 줄여야함 → parameter update is negative
양 : learning rate, ...
SGD, Adagrad, RMSprop, Adam 등의 optimizer이 있는데, 다음 포스팅에서 작성하겠다.
Model Evaluation
import torch
from torchmetrics import Accuracy
#Set up binary accuracy metric
acc = Accuracy(task="binary")
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for features, labels in dataloader_test:
# Get predicted probabilities for test data batch
outputs = net(features)
preds = (outputs >= 0.5).float()
acc(preds, labels.view(-1, 1))
# Compute total test accuracy
test_accuracy = acc.compute()
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_accuracy}")Weight Initialization
좋은 weight initialization
varience of layer input = varience of layer output
varience of gradients the same before and after a layer
He/Kaiming Initialization
원하는 varience 특성을 보장하는 weight initialization의 방법 중 하나

Batch Normalization(출력분포의 정규화)
After a layer :
1. Normalize output by
- subtracting mean
- dividing by the standard deviation
- i,e,. z val
2. Scale and shift normalized output using learned parameters
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9, 16)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(16, 8)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(8, 1)
# Add two batch normalization layers
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(16)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(8)
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.fc1.weight)
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.fc2.weight)
init.kaiming_uniform_(self.fc3.weight, nonlinearity="sigmoid")
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = nn.functional.elu(x)
# Pass x through the second set of layers
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = nn.functional.elu(x)
x = nn.functional.sigmoid(self.fc3(x))
return xbatch normalization 예시



